In mathematics, we generally solve various types of problems and for that, we also need a maths formulas list.
All formulas of maths make our problems easy.
And in this article, we are going to cover class 10th maths formulas chapter-wise for CBSE and MP Board students.
Let's start the list of maths formulas for class 10 (chapter-wise)
Real Numbers (Math formula class 10 chapter 1)
Euclid Division Lemma (Euclid's Division Algorithm)
→ Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
Or
→ a = bq + r, 0 ≤ r < b
HCF and LCM
→ HCF(a,b) × LCM(a,b) = a × b
Or
→ HCF × LCM = Product of both numbers
Algebraic Identities
→ (a+b)² = a² + 2ab + b²→ (a+b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3a²b + 3ab²
Law of Exponents (Exponents formulas list)
→ aᵐ × aⁿ = aᵐ⁺ⁿ
→ aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = aᵐ⁻ⁿ
→ aᵐ × bᵐ = (ab)ᵐ
Polynomials
The general form of Quadratic polynomial
ax² + bx + c = 0
Relationship between zeroes and coefficients-
→ Sum of zeroes-
α+β = (-b/a)
→ Product of zeroes
αβ = (c/a)
Division Algorithm
→ Dividend = (Divisor×Quotient) + Remainder
Or
→ p(x)=g(x)×q(x) + r(x)
Algebraic Identities
→ (a² - b²) = (a+b)(a-b)
→ (a² + b²) = (a+b)² - 2ab
Pair of linear equations in two variables
(Class 10 chapter 3 maths formula)
The general form of linear equation in two variables
a₁x + b₁y + c₁ = 0
a₂x + b₂y + c₂ = 0
Graphical Representation and Algebraic Interpretation
(a₁/a₂)≠(b₁/b₂)
→ Coincident lines and infinitely many solutions
(a₁/a₂)=(b₁/b₂)=(c₁/c₂)
→ Parallel lines and no solution
(a₁/a₂)=(b₁/b₂)≠(c₁/c₂)
Cross-multiplication method
→ x/(b₁c₂ - b₂c₁) = y/(c₁a₂ - c₂a₁) = 1/(a₁b₂ - a₂b₁)
→ Sum of two supplementary angles = 180°
Pythagoras theorem
→ H² = P² + B²
Speed, Distance, and Time Formulas
→ Speed = Distance/Time
→ Time = Distance/Speed
→ Distance = Speed×Time
Quadratic Equations (Class 10 maths chapter 4 all formula)
The general form of Quadratic Equation
ax² + bx + c = 0
Completing the Square method and List of Algebraic Identities (Class 10 algebra all formula)
→(a+b)² = a² + 2ab + b²
→ (a-b)² = a² - 2ab + b²
→ (a+b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3a²b + 3ab²
→ (a-b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3a²b - 3ab²
Quadratic Formula
{-b±√(b²-4ac)} / 2a
Nature of roots / Discriminant
→ Two distinct real roots, if
b² - 4ac > 0
→ Two equal real roots, if
b² - 4ac = 0
→ No real roots, if
b² - 4ac < 0
Formulas of Speed, Distance, and Time
Speed = Distance/Time
Time = Distance/Speed
Distance = Speed×Time
Arithmetic Progression (A.P.) (Arithmetic formula class 10)
The general form of A.P.
a, a+d, a+2d, a+3d, ..........a+(n-1)d
Nth term or Last term of A.P.
→ an = a + (n-1)d
Or
→ l = a + (n-1)d
Sum of n terms of an A.P.
→ Sn = (n/2){2a + (n-1)d}
Or
→ Sn = (n/2){a + an}
Or
→ Sn = (n/2){a + l}
Sum of first n positive integer
→ Sn = (n/2){n + 1}
Simple Interest
→ S. I. = (P×R×T)/100
Quadratic Formula
→ {-b±√(b²-4ac)} / 2a
Coordinate Geometry
Distance formula
√ {(x₂-x₁)² + (y₂-y₁)²}
Section Formula
x = (m₁x₂ + m₂x₁) / (m₁+m₂)
y = (m₁y₂ + m₂y₁) / (m₁+m₂)
Mid-point formula
x = (x₂ + x₁)/2
y = (y₂ + y₁)/2
Area of a triangle
(1/2){x₁(y₂-y₃)+x₂(y₃-y₁)+x₃(y₁-y₂)}
Or
(1/2)×Base×Height
Area of rhombus
=(1/2)D₁×D ₂
If points are collinear
(1/2){x₁(y₂-y₃)+x₂(y₃-y₁)+x₃(y₁-y₂)}=0
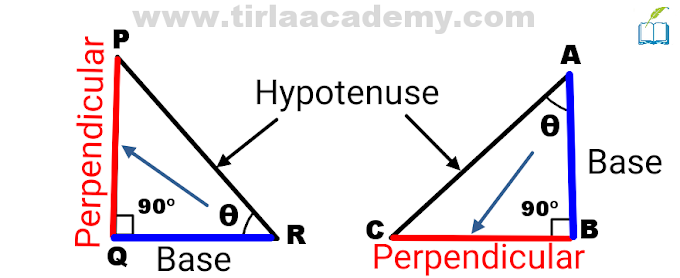
Introduction to Trigonometry
Some applications of Trigonometry
Trigonometry ratio formula class 10
sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, and cot.
→ sinθ = (1/cosecθ )
→ cosθ = (1/secθ )
→ tanθ = (1/cotθ)
→ cosecθ = (1/sinθ)
→ secθ = (1/cosθ)
→ cotθ = (1/tanθ )
→ tanθ = (sinθ/cosθ)
→ cotθ = (cosθ/sinθ)
Pythagoras theorem
H² = P² + B²
Trigonometric Ratio of Complementary Angles
→ sinθ = cos(90-θ)
→ cosθ = sin(90-θ)
→ tanθ = cot(90-θ)
→ cotθ = tan(90-θ)
→ cosecθ = sec(90-θ)
→ secθ = cosec(90-θ)
Trigonometric Identities
→ sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
→ sin²θ = 1 - cos²θ
→ cos²θ = 1 - sin²θ
→ sec²θ - tan²θ = 1
→ sec²θ = 1 + tan²θ
→ tan²θ = sec²θ - 1
→ cosec²θ - cot²θ = 1
→ cosec²θ = 1 + cot²θ
→ cot²θ = cosec²θ - 1
→ Sum of two complementary angles = 90°
Class 10 Areas related to circle formula
→ Area of Circle = πr²
→ Area of semi-circle = πr²/2
→ Circumference of circle = 2πr
→ Area of right-angled triangle = (1/2)×base×height
→ Area of equilateral triangle = √3side²/4
→ Area of square = side×side
→ Area of rectangle = Length×Breadth
→ Area of minor/major sector = (πr²θ)/360°
→ Length of Arc = (2πrθ)/360°
→ Area of minor/major segment = r²{πθ/360° - sin(θ/2)cos(θ/2)}
→ Perimeter of sector = (2πrθ)/360° + 2r
→ Area of circular ring = π(R²-r²)
→ Area of quadrant = πr²/4
Surface Area and Volume
→ Area of Circle = πr²
→ Area of circular ring = π(R²-r²)
Curved/Lateral Surface Area
→ Lateral surface area of cube = 4×edge²
→ Lateral surface area of cuboid = 2(bh+hl)
→ Curved surface area of cylinder = 2πrh
→ Curved surface area of hemisphere = 2πr²
→ Curved surface area of sphere = 4πr²
→ Curved surface area of cone = πrl
→ Slant Height of Cone l = √{h² + r²}
→ Curved surface area of a frustum of cone = πl(r₁ + r₂)
Total Surface Area
→ Total surface area of cube = 6×edge²
→ Total surface area of cuboid = 2(lb+bh+hl)
→ Total surface area of cylinder = 2πr(r+h)
→ Total surface area of sphere = 4πr²
→ Total surface area of hemisphere = 3πr²
→ Total surface area of cone = πr(l+r)
→ Total surface area of frustum of cone = πl(r₁ + r₂) + π(r₁² + r₂²)
Volume
→ Volume of cube = edge³
→ Volume of cuboid = L×B×H
→ Volume of cylinder = πr²h
→ Volume of sphere = (4/3)πr³
→ Volume of hemisphere = (2/3)πr³
→ Volume of cone = (1/3)πr²h
→ Volume of frustum of cone = (1/3)πh(r₁² + r₂² + r₁r₂)
→ Slant height of frustum of cone = √{(h²) + (r₁ - r₂)²}
→ 1 litre = 1000 cm³
→ 1000 litre = 1 m³
→ Speed = Distance / Time
Statistics class 10 formulas
→ Class Mark = (Upper class limit + Lower class limit) / 2
Mean
→ Direct method
x = ∑(fᵢxᵢ) / ∑(fᵢ)
→ Assumed mean method
x = a + ∑(fᵢdᵢ) / ∑(fᵢ)
→ Step-deviation method
x = a + {∑(fᵢuᵢ)/∑(fᵢ)}×h
Mode
l + {(f₁ - f₀)}h/{2f₁ - f₀ - f₂)
Median
l + {(n/2) - cf}×h / f
Empirical Formula
3 Median = Mode + 2 Mean
Probability
→ P(E) = (Number of outcomes favorable to E) / (Number of all possible outcomes of the experiments)
→ P(E) = 1 - P(not E)
→ Every Probability P(E) is-
0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1
Total possible outcomes in two dice
Here we are discussing the possible outcomes for two dice.
When we throw any two dice simultaneously, then we get the below results-
Face cards, Spades, Clubs, Diamond, Hearts, Ace, Jack, King, and Queen are shown in below picture-
How many playing cards are in one deck?
There are 52 playing cards in a deck.
How many face cards are there in a deck of 52 cards?
There are 12 face cards in a deck of 52 cards.
How many ace cards are in a deck of 52 cards?
There are 4 ace cards in a deck of 52 cards.
Now use the important formula of maths and solve your problems without any difficulties.